
Rehabilitation training for Parkinson’s disease is very important! Follow me and practice!

The treatment of Parkinson’s disease should adopt comprehensive treatment, individualized treatment and full-course management. Its main treatment methods include: drug therapy, rehabilitation therapy and surgical treatment, which are called the “three horses” of Parkinson’s disease treatment. Among them, drug therapy is the main one, surgical treatment is a beneficial supplement to drug therapy, and rehabilitation therapy can be carried out throughout the course of Parkinson’s disease.
Rehabilitation training for Parkinson’s disease is an important means to help patients maintain or improve their daily living abilities and improve their quality of life, mainly including the following aspects:
Basic rehabilitation – Training recommendations
No.1 Relaxation and breathing training
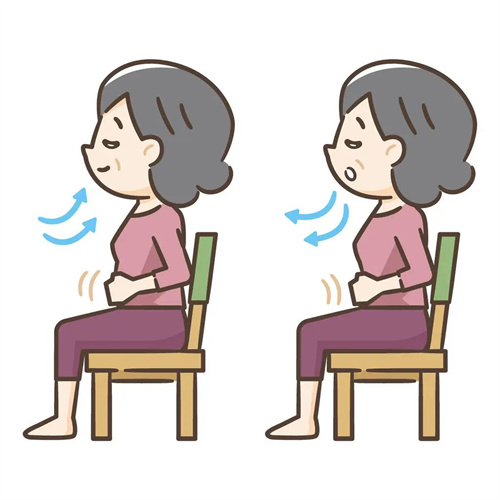
Practicing deep, slow breathing exercises, such as abdominal breathing, can help relax muscles throughout the body and reduce tension.
Repeat the exercise for 5-15 minutes to allow your body to gradually adapt and reach a relaxed state.
No.2 Facial movement training

In order to improve the stiffness of facial expressions, patients with Parkinson’s disease have a “mask face” that is unique to them. Exercises such as frowning, puffing cheeks, showing teeth, and whistling are performed.
Often make your face smile, laugh and other movements to increase the flexibility of your facial muscles.
No.3 Head and Neck Exercise
Tilt your head back and look at the ceiling for about 5 seconds, then lower your head and try to touch your chin to your chest.
Turn your head from side to side, turn to the right and look back to the right for about 5 seconds, then do the same to the left.
Repeatedly and slowly turn your face toward your left and right shoulders, and try to touch your shoulders with your chin.
Limb function – Training recommendations
No.1 Upper limb and shoulder exercises
Raise your shoulders towards your ears as far as possible, and then lower them as far as possible.
Straighten your arms, raise them above your head and hold them back for 10 seconds. Repeat.
Clasp your hands behind your back and pull them back for 5 seconds to strengthen the muscles of your upper limbs and shoulders.
No.2 Hand Exercise
Because the hands have many joints, Parkinson’s patients are more susceptible to muscle stiffness. Therefore, you should often straighten the metacarpophalangeal joints and flatten the palms.
You can use one hand to grab the fingers of the other hand and press toward the back of the hand to prevent metacarpophalangeal joint deformity.
Repeatedly practice the movements of spreading and closing your fingers, and quickly making a fist and extending your fingers.
No.3 Lower limb exercise
Stand with your legs slightly apart, bend your knees slightly, bend down, and try to touch the ground with your hands.
Hold the wall with your left hand, grab your right foot with your right hand and pull it back for a few seconds, then switch to the other side and repeat.
Gait training – Precautions
No.1 Basic Requirements
Ask the patient to look straight ahead and stand upright.
When starting, lift your toes as high as possible, landing on your heels first and then your toes.
The strides should be as slow and large as possible, and the upper limbs should be swinging back and forth as much as possible while walking.
No.2 Special Techniques
For patients who have “freezing” phenomenon, difficulty in starting to walk and panic gait, you can imagine that you are crossing a horizontal line or a pond on the ground. Once these phenomena occur, don’t be anxious, try to relax or stop and step on the spot for a few times before moving forward.
When walking outdoors, use the sidewalk tiles as a visual cue to determine how many tiles you must cross with each step.
Daily life – Activity
Training recommendations

Train patients to perform daily activities such as dressing themselves, going up and down stairs, washing, and going to the toilet.
Auxiliary facilities such as handrails and non-slip rubber cushions are added in rooms and bathrooms to improve patients’ safety and convenience.
Psychology – Guidance Cannot be ignored

Parkinson’s disease patients are often accompanied by mental symptoms such as depression and anxiety. Therefore, psychological counseling is also an important part of rehabilitation training.
By communicating with patients, encouraging and supporting them, we help them build confidence in overcoming the disease and maintain a happy mood.
Rehabilitation training for Parkinson’s disease patients is a comprehensive process that requires a personalized training program based on the patient’s specific situation and carried out under the guidance of professionals. At the same time, the patient’s family and caregivers should also actively participate in the rehabilitation training process and provide the patient with necessary support and help.
These 10 points are very important to control blood pressure
These days People with high blood pressure are always so “confident”
I’m so good at using the three consecutive rejections!
- “You have high blood pressure.”
- “No, I didn’t!”
- “You need to take medicine.”
- “I don’t need to eat!”
- “Not taking medicine can have serious consequences.”
- “Don’t talk nonsense!”
So
What should you pay attention to if you have high blood pressure?
How to effectively lower blood pressure?
Do you really know?
What are the update highlights?
Let’s take a look!
Recommended use
Electronic blood pressure monitor
The new “Guidelines” state that “the use of mercury sphygmomanometers is not recommended” and recommend the use of upper-arm electronic sphygmomanometers with verified accuracy.
When measuring blood pressure, repeat the measurement every 30 to 60 seconds and record the average of the two readings. If the difference between the two readings of systolic or diastolic pressure is more than 10 mmHg, measure again and record the average of the three readings.
Hypertensive patients
Pay attention to your heart rate
The Guidelines add “increased heart rate” to the risk factors affecting cardiovascular prognosis in patients with hypertension, and add “heart rate control” to the corresponding chapter on “treatment of related cardiovascular risk factors”.
The Guidelines define an increased heart rate in patients with hypertension as a resting heart rate > 80 beats/minute. If a patient with hypertension has an increased heart rate, the cause and reason should be promptly investigated.
Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption
Maintain healthy sleep
The new version of the “Guidelines” has added new recommendations on sleep in the chapter on therapeutic lifestyle interventions. Patients with hypertension should maintain healthy sleep and improve sleep disorders.
Lifestyle interventions proposed in the Guidelines
Healthy sleep includes adequate sleep duration and good sleep quality. Healthy sleep is associated with a lower risk of hypertension and, in hypertensive patients, with a lower incidence of coronary heart disease and stroke. Short sleep duration increases the risk of hypertension, and insomnia is associated with cardiovascular disease mortality and all-cause mortality.
The Guidelines recommend that all smokers quit smoking and avoid using e-cigarettes as much as possible to reduce hidden hypertension and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality.
People with high-normal blood pressure and hypertension should limit their long-term drinking.
Low sodium salt
The guidelines point out that all patients with hypertension should take various measures to limit their sodium salt intake. For those with good kidney function, it is recommended to choose low-sodium and potassium-rich salt alternatives.
Hypertensive patients
Exercise is essential
The “Guidelines” emphasize that for hypertensive patients with well-controlled blood pressure, mixed training is recommended, with aerobic exercise (walking, brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, etc.) as the main and resistance exercise as the supplement. It is also recommended to combine breathing training with flexibility and stretching training.
High blood pressure in the morning
Most dangerous
The Guidelines point out that morning hypertension is a strong predictor of target organ damage and cardiovascular risk, and that patients with morning hypertension have an increased relative risk of carotid atherosclerosis. If blood pressure is >135/85 mmHg when measured in the morning, it is considered morning hypertension.
The “Guidelines” recommend the use of truly long-acting drugs that can control blood pressure for 24 hours once a day to avoid poor control of morning blood pressure due to inappropriate treatment options.
Can assist in reducing blood pressure
3 major misconceptions
Don’t make this mistake~
Myth 1: Stop taking medication when blood pressure is normal
Blood pressure will rise again after stopping the medication, and intermittent medication is more likely to cause blood pressure fluctuations, causing more serious damage to organs such as the heart, brain, and kidneys.
At present, the medical community has not found a cure for hypertension, so patients with hypertension usually need to take antihypertensive drugs for life.
Myth 2: The faster and lower your blood pressure drops, the better
Except for hypertensive crisis, antihypertensive treatment should be carried out slowly so that blood pressure reaches the target in 4 to 12 weeks. If the blood pressure is lowered too quickly, hypertensive patients who have adapted to long-term high perfusion pressure may experience dizziness due to discomfort, which may lead to doubts about antihypertensive treatment.
If blood pressure drops too low, it will lead to insufficient blood flow to the brain and even induce a stroke. Therefore, antihypertensive treatment should not be too hasty or excessive.
Myth 3: No symptoms, no problem
High blood pressure can cause uncomfortable symptoms such as headache, dizziness, and head swelling, but some patients have had hypertension for a long time and their bodies have already tolerated the discomfort, so they may not feel anything.
It needs to be emphasized that the absence of discomfort does not mean that elevated blood pressure is not harmful to the body. By the time complications such as myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, cerebral hemorrhage, etc. occur, it is already too late.
“Healthy weight Ideal blood pressure
In addition to traditional risk factors for hypertension, such as increased life expectancy and high salt intake, metabolic-related risk factors (such as overweight and obesity) and psychological factors play an increasingly important role in the occurrence and development of hypertension.
01Preventing hypertension starts with a healthy lifestyle
① Reduce oil intake: Excessive intake of fat, especially foods high in saturated fatty acids, will increase blood cholesterol levels, lead to arteriosclerosis and increase the risk of hypertension. Daily diet should limit saturated fatty acid intake, while ensuring high-quality protein intake, increasing whole grains, coarse grains and dietary fiber intake, etc.
② Control your weight: Overweight and obesity can lead to high blood pressure and increase the risk of hypertension. Central obesity may have a stronger correlation with hypertension. It is recommended that overweight and obese people control their weight reasonably. The body mass index of adults aged 18 and above should be 18.5-23.9kg/m2 (body mass index = weight kg/height m2), and waist circumference should be reasonably controlled, male ≤85cm, female ≤80cm.
02 Manage hypertension by changing your behavior
① Reasonable diet: Adhering to a healthy diet helps control cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as hypertension. Hypertensive patients should adhere to a dietary pattern that is mainly plant-based and with a moderate amount of animal-based food, ensuring that the food is diverse, the energy supply ratio of the three major nutrients is appropriate, and the salt intake is not excessive.
② Moderate exercise: Regular exercise, adequate physical activity, and reduced sedentary time are important measures to control hypertension. It is recommended to focus on outdoor and aerobic exercise, with moderate-intensity aerobic exercise for at least 150 minutes per week. It is recommended to combine various forms of resistance (strength) training with flexibility training.
③ Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption: Smoking and drinking can increase the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. It is recommended that smokers quit smoking as early as possible (including traditional cigarettes and e-cigarettes), and patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as hypertension should not drink alcohol.
④ Psychological balance: Long-term mental stress, anxiety, depression, etc. can increase the risk of hypertension. You should maintain a positive and optimistic attitude, avoid negative emotions, and actively seek support and accept psychological intervention when necessary.
03 Scientific monitoring, stable blood pressure reduction, and long-term compliance
① Blood pressure target standard: The blood pressure of most hypertensive patients (including those with diabetes, coronary heart disease, heart failure or chronic kidney disease with proteinuria) should be controlled below 130/80 mmHg, and that of elderly patients aged 80 years and above can be controlled below 140/90 mmHg.
②Scientific monitoring of blood pressure: It is encouraged to monitor blood pressure at home, and dynamic blood pressure monitoring can be performed if conditions permit. Blood pressure should be measured in the morning after urination, before taking antihypertensive drugs, and before breakfast, and in the evening before going to bed. Each measurement should be performed 2-3 times according to the standard.
③ If blood pressure exceeds 130/80 mmHg, close attention should be paid. If blood pressure exceeds 140/90 mmHg three times on different days without taking antihypertensive drugs, it can be diagnosed as hypertension. Lifestyle intervention should be started as soon as possible and drug treatment should be taken as prescribed by the doctor. Patients with confirmed hypertension should adhere to long-term medication and are encouraged to choose long-acting antihypertensive drugs to ensure that blood pressure is steadily reduced to the standard level.
04 Comprehensive intervention, healthy weight
1. Self-monitoring of weight
a. Regularly monitoring weight changes is one of the important measures to prevent obesity.
b. Total weight gain after adulthood should be controlled within 5kg.
c. For overweight/obese individuals, weight gain should be controlled or weight should be reduced.
2. Eat a healthy diet
a. Focus on food intake diversification and balanced diet, and design a balanced diet under the premise of controlling total energy intake.
b. For overweight/obese individuals, reduce total energy intake by 500-1000 kcal per day on the basis of a balanced diet, or reduce total energy intake by 1/3 compared to the recommended intake.
c. Control the intake of high-energy foods (high-fat foods, sugary drinks and alcohol, etc.) and appropriately control the intake of carbohydrates.
d. When adopting energy-restricted dietary intervention, especially extremely low-energy dietary intervention, multivitamins and trace elements should be supplemented at the same time to prevent nutritional deficiencies caused by restricted diet.
3. Increase physical activity and exercise
Patients with well-controlled blood pressure are recommended to do aerobic exercise (moderate intensity, 30 minutes per day, 5-7 days per week), supplemented by resistance exercise (2-3 times per week), breathing and meditation, and a combination of flexibility training and stretching training. Patients with poorly controlled blood pressure (systolic blood pressure > 160 mmHg) are not recommended to do high-intensity exercise.
Note: Moderate to high intensity: can be determined by heart rate, subjective exertion or conversation test
-Heart rate: 40%~75% of heart rate reserve (HRR);
– Subjective feeling: Moderate intensity is a bit strenuous (not easy, but not very strenuous); high intensity is strenuous (feeling strenuous, but not to the point of exhaustion);
-Speech test: If you can speak at a normal rhythm during exercise but cannot sing, it is moderate intensity; if you cannot speak at a normal rhythm during exercise, it is high intensity exercise.
4. Behavioral intervention
Behavioral therapy, such as establishing diet awareness, making meal plans, recording the types and weight of food consumed, and calculating calories, can help reduce weight.
Weight loss plan should be adhered to for a long time
Speed varies from person to person
Don’t rush for success
Flu season is coming, are you ready?
From November to March of the following year, it is the peak season for influenza in northern my country. The flu season is coming, are you ready?
What is influenza?

Flu, the full name of influenza, is an acute respiratory infectious disease caused by influenza virus. Influenza virus is mainly divided into three types: A, B, and C. Among them, influenza A and B viruses are the most common and most contagious.
How influenza is spread
Influenza is mainly transmitted through droplets in the air (such as coughing and sneezing). It can also cause infection by touching objects contaminated with the virus and then touching the mouth, nose or eyes with hands.
Symptoms of the flu
Flu symptoms are usually more severe than the common cold and include:
① High fever (above 38°C, lasting 3-4 days)
② Headache and muscle aches
③ General fatigue
④ Sore throat and cough
⑤ Runny or stuffy nose
Some patients, especially the elderly, children or people with chronic diseases, may develop serious complications such as pneumonia, myocarditis, and even life-threatening conditions.
Flu Prevention
01Get a flu shot
Getting a flu shot every year is the most effective way to prevent the flu. The vaccine can reduce your risk of infection or lessen your symptoms.
02Maintain good personal hygiene habits
Wash your hands frequently, especially after touching public objects or crowded places; cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing.
03 Enhance immunity
Maintain a healthy lifestyle, such as a balanced diet, moderate exercise, and adequate sleep.
04Avoid contact with people with influenza
During the peak flu season, try to avoid crowded places.
Treatment of influenza
Flu is usually a self-limiting illness, and most people recover within one to two weeks. The following measures can help relieve symptoms:
① Get more rest and maintain your strength
② Replenish water to avoid dehydration
③ Use symptomatic medications (such as antipyretics, cough suppressants) to relieve discomfort
For critically ill patients, especially those with high-risk factors (children under 5 years old, elderly people ≥ 65 years old, women within 2 weeks after delivery, immunocompromised people, people with certain chronic comorbidities (including lung, heart, neurological, metabolic, hematological diseases, extreme obesity, etc.)), doctors may recommend the use of antiviral drugs, such as oseltamivir, mabaloxavir, etc., to reduce the course of the disease and the risk of complications.
Influenza is a highly contagious respiratory disease
Although most patients have mild symptoms
But for the elderly, children and people with weakened immune systems
Flu can cause serious health problems
Get a flu shot every year
Maintain good hygiene habits
It is a key measure to prevent influenza
Are your eyes red, swollen, itchy, and painful? Don’t panic! Learn how to identify and treat allergic conjunctivitis!
What is allergic conjunctivitis?
Allergic conjunctivitis is a type of illness caused by a hypersensitivity reaction of the conjunctiva to allergen stimulation. It is divided into seasonal allergic conjunctivitis, perennial allergic conjunctivitis, vernal keratoconjunctivitis, giant papillary conjunctivitis, and atopic keratoconjunctivitis.
Seasonal allergic conjunctivitis is mainly a hypersensitivity reaction and is also the most common type of allergic conjunctivitis.
What are the causes of allergic conjunctivitis?

Allergic conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by contact with allergens. There are many allergens that cause allergic conjunctivitis, which are widely present in our lives, and pollen is the most common allergen.

Secondly, cosmetics, contact lenses, foreign bodies implanted during eye surgery, pets, dust mites and dust particles in the air that we come into contact with on a daily basis are also allergens.

In addition, patients who have suffered from eczema, allergic rhinitis, low immunity, etc. often suffer from allergic conjunctivitis.
Allergic conjunctivitis has a genetic tendency, and it is more likely to occur if parents have a history of allergic conjunctivitis.
What are the symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis?
01 The most common symptoms: itchy eyes and conjunctival congestion, i.e. redness of the whites of the eyes.
02 Other symptoms: red and swollen eyelids; dry eyes, foreign body sensation, burning sensation, patients may blink and rub their eyes frequently; tearing, fear of light, increased secretions (secretions are mostly mucous and sticky and thread-like); severe allergic conjunctivitis, sometimes accompanied by decreased vision.
What is the difference between allergic conjunctivitis and common conjunctivitis ?
Allergic conjunctivitis is also a type of conjunctivitis, so like other types of conjunctivitis, symptoms include red eyes and increased secretions.
However, the main symptom of allergic conjunctivitis is itchy eyes, and the more you rub the eyes, the more itchy they become; in ordinary conjunctivitis, the symptoms of itchy eyes will be relieved after rubbing the eyes.
In addition, the secretions of allergic conjunctivitis are also different from those of other conjunctivitis. The secretions of allergic conjunctivitis are relatively sticky and stringy, while ordinary conjunctivitis has a large amount of yellow-white secretions.
How is allergic conjunctivitis treated?
The treatment principles of allergic conjunctivitis include health education, avoiding allergens, and alleviating the patient’s symptoms and signs. For most patients, the main focus is on relieving discomfort such as itchy and red eyes; while for patients with long-term attacks or prolonged illness, the main focus is on controlling the inflammatory response state. Treatment mainly starts from two aspects.
General treatment measures
01

Avoiding allergens: This is the most effective treatment, but is often difficult to achieve in practice.
Try to avoid or reduce contact with possible allergens, keep the living environment clean and hygienic, ventilate frequently, and take protective measures when going out, such as wearing goggles and masks. Wash your hands and face in time after returning home.
Stop wearing contact lenses during allergy season.
02

Cold compress on the eyes: Apply ice to the eyes to lower the local temperature of the eyes, reduce the activity of allergic cells, reduce the release of allergic substances, and relieve allergic symptoms.
03

Wear dark glasses: reduce sunlight stimulation and avoid rubbing your eyes.
04
Rinse the conjunctival sac with normal saline: Rinse with normal saline can neutralize the pH value of tears and dilute the antigens in tears.
05

Improve your own resistance: Allergic conjunctivitis is mostly related to your physical constitution. A regular lifestyle, a healthy and reasonable diet, and proper physical exercise can help enhance your resistance to allergic substances.
06

Allergic conjunctivitis is mostly self-limiting. As the patient ages, the body adapts to the environment, and resistance increases, the allergic symptoms will be alleviated.
To prevent respiratory illness, wear masks correctly
1. It is recommended to wear a mask in the following situations:
★ During the period of flu-like symptoms such as fever, sore throat, cough, etc.;
★ When going to medical institutions for consultation, accompanying, nursing or visiting;
★ When key groups such as the elderly, children, patients with chronic diseases, and pregnant women take public transportation or go to crowded places;
★ It is recommended that outsiders enter places where vulnerable groups gather, such as nursing homes and social welfare institutions, and public service personnel wear masks while working.
2. How to wear a mask?
For citizens, if there are no special occupational needs, medical surgical masks can provide good protection in general life and work scenarios .
Before wearing a mask, keep your hands clean. When wearing it, distinguish the inside and outside, top and bottom by the color depth, wrinkle direction, and metal strip position.
After wearing it, pull the folds up and down to ensure that the mask can cover the mouth, nose and chin. Press the metal strips with both hands to make the mask fit better with the face and maintain airtightness.
We must insist on wearing masks scientifically. Some people have the habit of pulling down the mask to expose their nose when wearing it, which will affect the protective effect of the mask.
3. Daily wearing of masks by the public – How often should it be changed?
★ When citizens wear masks, if they become wet or dirty, they should change them immediately.
★ Under normal circumstances, it is recommended that the cumulative wearing time of each mask does not exceed 8 hours , and everyone is reminded to replace the mask in time.
During the peak season for respiratory infectious diseases, how should the elderly protect themselves?
Currently, respiratory diseases have entered a high incidence period. Although children are more likely to be infected, the elderly are susceptible to respiratory infections and have a higher chance of developing severe symptoms after infection, so they also need to strengthen prevention.
01
Why is it easy for the elderly to
Got a respiratory infection?
Whether a respiratory infection will occur after pathogens enter the human body and its severity is determined by the body’s resistance and the confrontation between the pathogens, one good and one evil. The elderly have a decline in lung function, reduced local and systemic immunity in the respiratory tract, and aging of cellular immunity, humoral immunity, innate immunity, and acquired immunity due to aging, which can all make them more susceptible to respiratory infections. In addition, the elderly often have multiple underlying diseases or the use of immunosuppressive drugs due to disease can also weaken the patient’s immune function.

02
Current respiratory infections
Which pathogen is the main one?
At present, the most common respiratory infectious diseases are influenza, mainly subtype A H3N2, and other pathogens include rhinovirus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus, etc. The infection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae is gradually declining. Influenza virus, human metapneumovirus and common coronavirus are the main infectious diseases in the elderly, and some patients are mixedly infected with multiple pathogens.
03
Respiratory tract infection in the elderly
What are the clinical manifestations?
Typical symptoms of respiratory tract infection include upper respiratory tract symptoms, fever, cough, body aches, fatigue, etc. Patients with concurrent lung infection may have symptoms such as expectoration and chest pain. It is important to be aware that some elderly people often have atypical symptoms after respiratory tract infection, including the lack of typical respiratory tract infection symptoms, symptoms such as the pentad of geriatric diseases (falls, altered mental status, incontinence, autonomous activity, loss of appetite), and unexplained aggravation of the primary disease.
Therefore, when elderly people experience changes in mental state, a significant decrease in food intake, a significant decrease in independent activity, or even falls, they need to be alert to the possibility of respiratory infection and seek medical attention as soon as possible to avoid delaying the disease.

04
How can the elderly prevent
Respiratory tract infection?
Prevention of respiratory infections in the elderly includes two aspects: basic prevention and vaccination.
1. Basic prevention
It is still necessary to maintain the hygienic habits of wearing masks, ventilating more, and washing hands frequently. Take personal protection when you have respiratory symptoms, avoid close contact with other relatives at home, open windows for ventilation 2-3 times a day, each time for at least 30 minutes. When opening windows for ventilation, pay attention to keep warm and avoid “drafts”. Respiratory secretions should be sealed and discarded in time.
Nursing homes need to do a good job of disinfection and hygiene, reduce gatherings, and reduce unnecessary visits. Visitors need to wear masks for protection during visits.
2. Vaccination
Vaccination is a safe and effective preventive measure for the elderly. Flu vaccines need to be administered every year, usually before the flu season arrives in October, because it takes 2-4 weeks for the body to produce protective antibodies after the flu vaccine. Patients who are allergic to vaccine ingredients cannot be vaccinated. Elderly people who are in the acute stage of chronic diseases need to postpone vaccination and consider vaccination after their condition stabilizes.
05
Elderly people accidentally get sick
what to do?
If the elderly accidentally fall ill, don’t panic. First, they need to identify the recent illness of their relatives or friends with whom they have had close contact.
If you have been in contact with influenza patients and have related symptoms, you can go to a community health center or hospital for pathogen testing and receive targeted treatment, and take medication within 48 hours of the onset of influenza. If it is a viral infection such as rhinovirus or adenovirus, there is usually no targeted antiviral treatment, and only medication for respiratory symptoms is needed to relieve discomfort.
Elderly people with underlying diseases need to seek medical treatment in a timely manner. Patients who do not seek medical treatment in time need to be closely monitored for changes in their condition, including changes in body temperature, respiration, pulse, blood pressure, etc. If conditions permit, a finger-clip pulse oximeter can be used at home to monitor pulse oxygen saturation. If the patient has a high fever, or the temperature does not subside for 3 days, shortness of breath, faster or slower heart rate, irregular rhythm, significantly increased or decreased blood pressure, pulse oxygen saturation ≤93%, mental depression or even mental disorder, and poor food intake, they need to be sent to the doctor in a timely manner.

06
After rehabilitation of the elderly
How to recover?
Elderly people recover more slowly from respiratory tract infections than young people. After symptoms improve, they still need to eat easily digestible and nutritious food according to their own spleen and stomach function, pay attention to balanced nutrition, meat and vegetable combination, and avoid spicy and stimulating food. Elderly people’s renal function declines with age, so do not blindly supplement albumin. Elderly people may have problems such as decreased mobility after respiratory tract infection, and need to exercise step by step. They can use walkers to move around at home. They must prevent secondary injuries caused by falls, and do not rush to go out for strenuous physical exercise. They need to keep warm when going out. For bedridden elderly people, pay attention to turning over and patting their backs, strengthen respiratory care, and pay attention to whether the patient has swallowed the food completely when eating to prevent aspiration.
Home care of the pocket after permanent pacemaker implantation in elderly patients
What is a pacemaker?
A pacemaker is an electronic therapeutic device that is implanted in the body through a minimally invasive method. It emits electrical pulses powered by batteries through a pulse generator. In short, it is a device that can make the heart beat.
What problems may occur with the permanent pacemaker pocket?
Pacemaker pocket complications include pocket bleeding, pocket hematoma, pocket infection and pocket rupture, which are progressive and gradually worsening processes. If not handled in time or measures are not in place, pocket rupture may be induced, leading to systemic infection and the removal of the entire pacing system, increasing the difficulty of clinical treatment and the economic burden on patients.
Pocket bleeding can be rapid or slow. If it is rapid bleeding, there will be pain, soreness and discomfort, and the pacemaker pocket will bulge rapidly, which is easy to detect.
However, if the sac oozes blood slowly, the symptoms of distension and pain are not obvious, and the sac gradually bulges, it is easy to be ignored and often not discovered until the sac is infected. Therefore, after permanent pacemaker implantation, it is crucial to observe the skin at the sac and identify bleeding and infection at an early stage.
3. What are the risk factors for permanent pacemaker pocket infection in elderly patients?
1. Elderly and frail, with other chronic diseases. This is related to the elderly patients’ thin body, poor nutritional status, relatively low immune function, and reduced wound repair ability.
2. Pocket hematoma. Pocket hematoma is one of the main causes of pocket infection. Elderly patients often have cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, take anticoagulants for a long time, have thin subcutaneous tissue and loose skin, and are prone to “dead space” in the pocket, which increases the chance of pocket hematoma. Pocket hematoma is confined to the pocket and is therefore difficult to absorb.
3. It is related to improper size and location of the pouch and pacemaker replacement at the same location.
4. What are the precautions for home care of the pouch after permanent pacemaker implantation in elderly patients?
1. Pay attention to the skin condition of the pouch area. If the pouch area has bleeding, hematoma, local redness, swelling, heat and pain, fluctuation when touched, and secretions seeping out, it indicates pouch bleeding and infection, and you should go to the hospital for treatment in time.
2. Avoid strong friction. For elderly patients, especially those who are weak and thin, they should pay attention to protecting the skin of the sac area during daily activities and bathing, and avoid strong friction, such as rubbing the skin of the sac area vigorously when scrubbing the bath, so as to avoid bleeding and infection.
3. Diet and lifestyle care. Strengthen nutritional support and appropriately supplement high-quality protein and high-fiber foods, such as soy products, fish, beef and fresh vegetables. Diabetic patients should monitor blood sugar regularly, control blood sugar levels, and eat small meals frequently. Develop good living habits, maintain a regular work and rest schedule, avoid staying up late, overeating and other bad habits, etc., so as to improve the patient’s overall condition and enhance the patient’s immunity.
4. Psychological care. After permanent pacemaker implantation in elderly patients, caregivers should provide adequate social and psychological support to enable patients to maintain a positive and optimistic attitude and cooperate with treatment and care.
How to prevent pressure sores in bedridden elderly people

At work, we often hear people like this: “My elderly family member has been bedridden for many years, and what I fear most is bedsores!” The “bedsores” that everyone talks about have a professional name – pressure injury, which refers to local damage to the skin and/or subcutaneous tissue caused by pressure or pressure combined with shear force. It often occurs at bony protrusions, but may also be related to medical devices or other objects.
Once a pressure sore occurs, it will not only increase the patient’s pain and burden on the family, but may even threaten life. So, how can we prevent the occurrence of pressure sores in bedridden elderly people? Please follow my instructions:
01Change body position in time

Changing body positions is the most common way to avoid continuous pressure in the same position. Caregivers need to design a daily body position change plan for the elderly based on their activity level, limb flexibility, ability to change body positions independently, skin and tissue tolerance, and overall health status, and increase attention to changing body positions.
02Protect bony prominences

Avoid prolonged pressure on bony protrusions. For example, the heel is one of the most common sites of pressure injuries. For daily care, you can use a pillow or foam pad to elevate the heel to disperse the pressure along the calf and achieve complete decompression of the heel. You can also use medical foam dressings to protect bony protrusions.
03 Keep the bed flat.
Clean, dry and free of debris

Wet bedding can soak the skin and cause prolonged irritation, increasing the risk of pressure sores.
04Keep your skin clean and properly moisturized

Clean the skin immediately after defecation and avoid using alkaline soaps and detergents. Use isolation products to protect the skin from moisture and avoid rubbing the skin vigorously. It is recommended to use highly absorbent urinary incontinence products, textiles with a low coefficient of friction, and silicone foam dressings to protect the skin.
05 Care should be gentle

When turning the patient over, avoid dragging, pulling, or tugging. If necessary, multiple people can operate or use tools to change the position, such as using a turning pad, sponge pad, soft pillow, etc. Tip: When turning over, a 30° side-lying position is better than a 90° side-lying position, and keep the patient’s bed head as flat as possible. Encourage patients who can change their position independently to sleep in a 20-30° side-lying position. When the head of the bed must be raised (such as to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia), keep it at 30° or lower.
06Suitable temperature and humidity

The living environment should have appropriate temperature and humidity to avoid excessive dryness or humidity of the skin, which may cause eczema and other skin problems.
07Improve body nutrition

It is recommended to conduct a comprehensive nutritional assessment and develop a personalized nutritional plan for the elderly who are at risk of or have already suffered pressure injuries. Maintain a certain amount of subcutaneous fat to increase skin elasticity and prevent pressure sores.
08 Check the decompression tools in time

When using decompression tools for a long time, such as air mattresses and turning mats, the performance and effectiveness of the equipment should be checked regularly. We can check the airtightness of the air mattress pipeline connection every morning and adjust the pressure at any time according to the patient’s condition to maintain the patient’s comfort.
09 Raise awareness

When bedridden elderly people develop fever, weight loss, edema, or abnormal skin color in local pressure areas, be alert to the possibility of pressure ulcers and pay more attention to local tissue changes.
How can the elderly avoid aspiration during daily eating?
Preface
Recently, the department successfully treated an elderly patient who suffered from dyspnea and hypoxemia due to accidental inhalation of garlic cloves. The patient was in a critical condition. After emergency treatment, the doctor successfully removed the garlic cloves under bronchoscope and the patient was out of danger. In fact, such cases are very common among the elderly. Common foreign bodies include inhaled teeth and jujube pits. Why does this happen?
Elderly people may suffer from respiratory failure, cerebrovascular accident, weakness, sedative medication, etc., which may cause a decrease in cough reflex and incomplete glottal closure, leading to accidental inhalation of food, oropharyngeal secretions, or gastroesophageal reflux into the airway, causing lung infection or suffocation, and even endangering life. So how can we avoid aspiration during our daily eating?
01 Eating status assessment

Pay attention to changes in the elderly’s eating habits. When the elderly choke when eating, take a long time to eat, chew weakly/slowly, have difficulty swallowing, or have food residue or food boluses left in the mouth after eating, caregivers should be alert and investigate the reasons for the changes in the elderly’s eating habits. If necessary, go to the hospital for further examination.
02 Requirements for eating posture
Generally speaking, the patient should sit upright with the trunk straight and the head slightly tilted forward. For bedridden elderly people, caregivers can help raise the head of the bed 30 degrees or use soft pillows or cushions to maintain a sitting position. If the patient is unable to complete the above actions, the patient can choose to lie on the healthy side or tilt the head to one side.
03 Eating environment

The elderly should concentrate on eating and should not be distracted by talking or watching TV or playing with mobile phones while eating. Try to avoid noise or sudden movement of people while the elderly are eating.
04 Eating tools

It is recommended that elderly people with swallowing disorders use small, shallow spoons to facilitate the delivery of food to the mouth and avoid eating too large a bolus at one time. If the elderly have difficulty opening their mouths, they can also choose a bottle or nasogastric syringe to deliver liquid food such as fruit puree and rice paste into the mouth.
05 Food Choice
Dynamically adjust the elderly’s dietary structure. When it is known that a certain food may cause choking or swallowing difficulties in the elderly, we should pay great attention to it, avoid choosing food in similar forms, and change the cooking method of the ingredients.

For example, some elderly people like to eat beef very much, but the fibers of beef chunks are coarse and it is not easy for the elderly to chew and swallow. We can make beef balls, meat puree, etc. for easy eating; if the elderly choke when drinking water, we can use a special thickener to change the viscosity of the liquid to make it easier for the elderly to drink safely.
06 Eating process
01

Avoid eating too fast and putting too much food in your mouth at one time.
Be sure to chew slowly and thoroughly, swallow one bite at a time before eating the next, and do not rush the elderly to eat.
02
Break up large chunks of meat into smaller, chewable pieces.
03

Before eating, cut long pieces of food that are difficult to bite off into pieces, or cut them into small pieces that are easy to swallow when cooking. Avoid eating vegetables and long leafy vegetables that contain crude fiber.
04

When eating fruits with pits, chewing bones or eating fish, check carefully to avoid fruit pits, small bones, fish bones, etc. from accidentally entering the airway.
05

If choking or coughing occurs while eating, you should stop eating immediately and resume eating after the coughing stops completely.
06

Check your mouth for any food residue after eating and rinse your mouth after each meal.
07 Identification of aspiration

According to the manifestation of aspiration, it can be divided into overt aspiration and covert aspiration. Overt aspiration is accompanied by sudden respiratory symptoms such as coughing and voice changes after swallowing, and dyspnea is the first and most prominent manifestation.
Hidden aspiration is often not detected until the elderly develop aspiration pneumonia, which is often manifested as mental depression, apathy, slow reaction, fever, etc. Further examination and tracing of the cause reveal that it is caused by aspiration.
Therefore, if you find severe choking during/after eating, or if the elderly still have coughing, wheezing, hoarseness, difficulty breathing, cyanosis, fever, etc. after a brief relief from choking, you should go to the hospital for treatment as soon as possible.
Conclusion
Once again, we remind the family members and caregivers of the elderly to pay attention to the safety of the elderly’s eating. In case of aspiration, the Heimlich maneuver can be used for emergency treatment, and if necessary, go to the hospital for comprehensive examination and treatment.
Vegetables come in many colors, eat a wide variety and get enough nutrition

There are many kinds of vegetables, and they are one of the important nutritious foods in people’s lives. They are brightly colored, delicious, and rich in vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber, and natural antioxidants necessary for the human body. They play a special role in human health.
Fresh vegetables are an important source of vitamin C, carotene and B vitamins in the diet. Vegetables are rich in minerals, such as calcium, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, iron, copper, sodium, etc. They are alkaline foods and play an important role in maintaining the acid-base balance in the body.
It is good for the health of the elderly to eat more vegetables, but in real life, many elderly people often do not eat enough vegetables due to dental or other reasons, and the variety of vegetables they eat is also very limited. The “Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents (2022)” recommends that the elderly consume 300-500 grams of vegetables per day, preferably half of which should be dark vegetables, and ensure that there are 1-2 kinds of vegetables at each meal, and pay attention to the combination of types and colors.


Scientists have found that the nutritional value of vegetables is closely related to their color. According to the depth of color, vegetables can be divided into dark vegetables and light vegetables.
Dark vegetables usually refer to dark green, red, orange-red and purple-red vegetables. The darker the color of the vegetables, the more nutritional advantages they have.
green vegetables
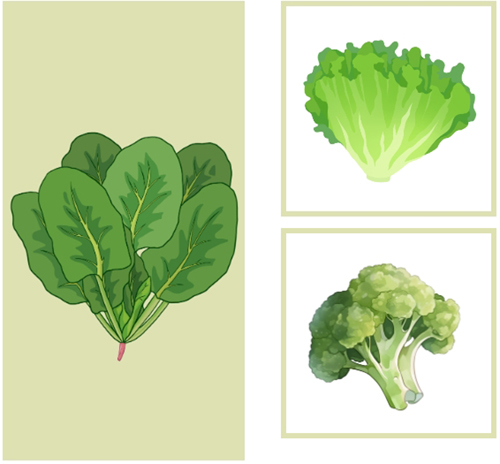

Green vegetables are the most common in daily life, mainly spinach, rapeseed, lettuce, romaine lettuce, broccoli, etc. Green vegetables give people a bright and fresh feeling, have a certain sedative effect on people with high blood pressure and insomnia, and are also good for the liver. Green vegetables contain tartaric acid, which can prevent sugar from turning into fat. Overweight and obese people can eat more green vegetables. In addition, green vegetables are also rich in nutrients such as folic acid, calcium, and selenium.
Yellow vegetables

The greatest nutritional value of yellow vegetables is carotene, vitamin C, and vitamin A. For people with poor appetite, it can increase appetite and moisturize the skin. Representative vegetables of yellow include carrots, yellow peppers, pumpkins, and golden gourds.
Red vegetables

Red vegetables mainly include tomatoes, red peppers, red sweet potatoes, etc. They give people a striking and exciting feeling, can increase people’s appetite and stimulate the excitability of the nervous system. Red vegetables are also rich in carotene, vitamin C and vitamin A.
Purple vegetables

The biggest feature of purple vegetables is that they contain the legendary antioxidant artifact – anthocyanin, which can prevent cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. The representative vegetable is purple cabbage, and there are also purple eggplant, perilla, cowpea, purple bean, etc.
White vegetables
Vegetables mainly in white color include wild rice stem, lotus root, bamboo shoots, winter melon, oyster mushroom, cauliflower and white radish. They give people a feeling of cleanliness, coolness and freshness. They play a certain role in regulating visual balance and calming emotions. They are also beneficial in preventing and treating hypertension and myocardial diseases.
Black vegetables

Vegetables that are mainly black include hair algae, kelp, black fungus, black sesame, etc. They give people a rustic, strong taste and a strong feeling. Black vegetables can stimulate the endocrine system, promote saliva secretion, benefit gastrointestinal digestion and enhance hematopoietic function. Studies have shown that the active substances in black fungus can inhibit tumor cells and reduce the incidence of cancer.

Different vegetables contain different nutrients, so in daily life we need to eat a wide range of vegetables and eat vegetables of different colors at the same time to make up for their shortcomings, balance nutrition and stay healthy.
In addition, colorful vegetables not only satisfy the taste buds, but also satisfy the eyes, which helps to increase appetite, add fun and prolong life.
How much do you know about home oxygen therapy?

Home oxygen therapy refers to the method of providing oxygen therapy in a home environment to relieve hypoxia symptoms and promote health. Studies have shown that long-term home oxygen therapy can correct hypoxemia, reduce the damage of hypoxia to important organs such as the heart, brain, kidneys, and lungs, and improve the quality of life.
Who is suitable for home oxygen therapy?
Not everyone needs long-term home oxygen therapy. Generally speaking, for the elderly, COPD patients, or elderly people with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, if oxygen inhalation can improve the hypoxia state, the doctor will recommend a home oxygen therapy plan such as appropriate oxygen therapy concentration, oxygen therapy time, and oxygen delivery method by evaluating the condition, airflow obstruction, lifestyle, and treatment compliance.
What equipment is needed for home oxygen therapy?
Oxygen breathing device
①Double-lumen nasal cannula :
The advantages are that it is convenient and does not affect eating. It is suitable for patients with mild to moderate reduction in oxygen partial pressure or oxygen saturation.
Instructions:
Connect it to the air supply end of the device, adjust the oxygen flow, check that the pipeline is unobstructed before wearing it. When using it, be careful not to tie it too tight to avoid compressing the skin around the ears and cheeks.
②Oxygen mask:

It is suitable for patients who breathe through their mouths, have nasal diseases that affect oxygen inhalation, and have high requirements for oxygen concentration.
Instructions:
Cover the mouth, nose and chin with the mask, fix the flexible metal strip on the bridge of the nose, and adjust the elastic band to ensure the patient’s comfort.
2 Oxygen supply device
① Compressed oxygen cylinder:
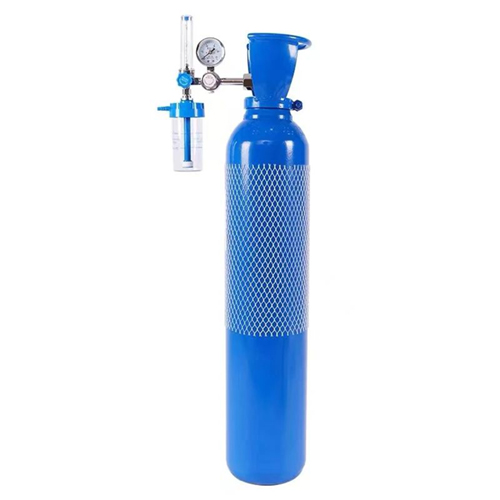

There are many ways to buy home oxygen cylinders. You can buy products that meet production and use standards through pharmacies, medical equipment stores or e-commerce platforms. However, oxygen cylinders are large in size and heavy in weight, and require regular refilling or replacement of oxygen. It is recommended that before purchasing, you should consult the merchant about “oxygen cylinder filling and other after-sales services” to ensure the continuity of subsequent home oxygen therapy.
②Oxygen concentrator (commonly known as oxygen concentrator):

Home oxygen concentrators are easy to operate, portable, and can produce oxygen continuously. You only need to regularly test the oxygen flow and concentration. When purchasing, you should consider the reliability, safety, economy, and portability of the equipment. You can refer to the “Home Oxygen Concentrator” industry standard (QB/T 5368?2019) approved and issued by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and be sure to choose a regular manufacturer with complete qualifications.
Oximeter
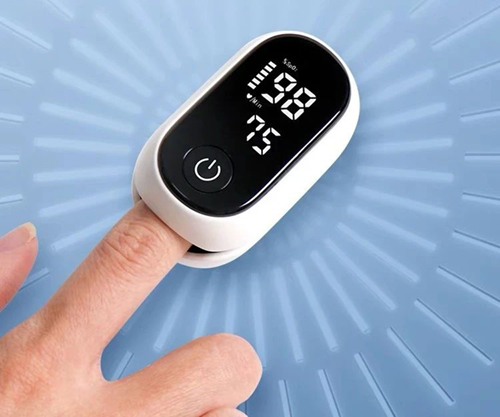

Home oxygen therapy can be equipped with a finger-clip oximeter to monitor blood oxygen saturation and heart rate. It is recommended to purchase one that meets national safety standards and quality requirements, and pay attention to the measurement range, accuracy and stability of the equipment.
Home oxygen therapy precautions
1. Follow the doctor’s advice and carry out home oxygen therapy regularly
When using oxygen at home, you need to adjust the oxygen flow and oxygen therapy time according to the doctor’s advice.
2. Ensure humidification effectiveness
To avoid dry oxygen irritating the nasal cavity and respiratory tract, it is very important to increase humidification. When breathing oxygen at home, you can buy pure water and pour it into the humidification cup to achieve the humidification effect.
3. Pay attention to observation
During oxygen inhalation, pay attention to pulse, blood pressure, mental state, skin color, humidity and breathing pattern. If you feel that the symptoms of hypoxia cannot be relieved, please seek medical attention in time.
4. Prevent infection
Oxygen inhalation devices and humidification bottles must be strictly cleaned and disinfected, replaced regularly, and used by designated personnel to avoid the growth of mold and bacteria, and to prevent cross infection and secondary infection.
5. Improve oxygen safety
Oxygen can help combustion, so when performing oxygen therapy, be careful to keep the oxygen concentrator away from fireworks and flammable materials. Families using oxygen cylinders should avoid tipping and bumping when moving them to prevent explosions.
Let’s talk about high blood pressure and heart rate
Hypertension is a common and frequently occurring disease worldwide, which can cause target organ damage in multiple organs and seriously threaten human health. For this reason, on April 7, 1978, the World Health Organization and the International Federation of Societies of Cardiology decided to designate May 17 of each year as “World Hypertension Day” to draw people’s attention to hypertension.
May 17th this year is the 10th World Hypertension Day. The theme of this year’s event is “Healthy Blood Pressure, Healthy Heartbeat”.
What is the connection between blood pressure and heart rate? Experts explain in detail:
Understanding Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
Blood pressure is the lateral pressure exerted on the blood vessel wall when blood circulates in the blood vessels. The regulation of blood pressure is a complex process, which mainly depends on the amount of blood discharged by the heart and the resistance of blood vessels. When the heart contracts, the blood in the heart is discharged into the blood vessels, and when the heart relaxes, the blood in the blood vessels returns to the heart, and the cycle repeats.
One heartbeat is when the heart completes one contraction and one relaxation. The amount of blood pumped by the heart is related to blood volume, myocardial contractility, and heart rate. If our vascular resistance increases and blood pressure rises, the heart needs a stronger heartbeat and a faster heartbeat to ensure blood circulation throughout our body.

Blood pressure and heart rate are closely linked
When the patient experiences symptoms such as palpitations, intermittent heartbeats, palpitations after activity, and intolerance to activity; when the electrocardiogram shows a rapid heartbeat, irregular heart rate, premature beats, etc., the doctor will consider whether the patient may have high blood pressure.
Sometimes the patient’s heart rate is not fast, but there is a strong sense of panic, increased myocardial contractility, too strong heartbeat and other symptoms, it is also necessary to consider whether there is hypertension. For example, some patients hear their heartbeats very strongly when they sleep (which they could not hear before), or feel the blood vessels in their heads pulsating when they lie down.
Although some patients who feel anxious during activities do not have high blood pressure in daily measurements, their blood pressure rises rapidly during exercise. At this time, they should pay attention to preventing exercise-induced hypertension. Exercise-induced hypertension often indicates the emergence of new hypertension.
High blood pressure, fast heartbeat
What are the hazards to the heart
Hypertension can cause symptoms such as tachycardia, strong heartbeat, irregular heartbeat and premature beats. In addition to causing discomfort, long-term tachycardia may lead to decreased heart function and heart failure. Strong heartbeat is caused by excessive myocardial contraction. Long-term excessive myocardial contraction can lead to myocardial hypertrophy, which in turn leads to myocardial diastolic dysfunction and even hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
When blood pressure rises, the heart will increase the pressure in the heart chambers to ensure effective blood circulation throughout the body. The heart is divided into atria and ventricles. The muscles of the atria are relatively thin, so the pressure increase in the atria is more significant, and arrhythmias such as atrial premature beats and atrial tachycardia may occur. If blood pressure is not controlled for a long time, the atria will be under high pressure for a long time, leading to atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation; long-term high atrial pressure may also lead to atrial enlargement, increasing the risk of heart failure and thromboembolism.
How to Maintain Healthy Blood Pressure
In order to stay healthy, adults should adopt a reasonable diet and good living habits, and monitor their blood pressure at least 1-2 times a year. If diagnosed with hypertension, we also need to fully evaluate whether there are other cardiovascular and cerebrovascular risk factors related to hypertension, and evaluate whether there is target organ damage caused by hypertension. Based on individual conditions, choose antihypertensive drugs that are suitable for you to control your blood pressure at an ideal level and keep your heart rate at an ideal level. Let us work together to maintain a healthy blood pressure and heartbeat.
Alzheimer’s disease discharge health prescription
Medical
1. Although there is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, early detection and appropriate intervention can significantly improve the quality of life of the elderly with the disease, and patients can still enjoy life within their capabilities for a long time. According to the evaluation results of the doctor or nurse on the patient at discharge, the patient’s ability to live may be mildly dependent, moderately dependent or severely dependent, requiring a small amount of care, a large part of care or complete care respectively. You can choose home care or enter a suitable nursing home based on your family’s manpower and financial situation.
2. After discharge, family members or other caregivers should pay attention to changes in the patient’s intelligence, behavior, and mood. If the symptoms are relatively stable, the elderly can be taken for a follow-up visit every three months as instructed by the doctor; if there are obvious changes in the condition, such as suddenly becoming more “confused”, dangerous behaviors such as attacking or self-harming family members or themselves, abnormal excitement or depression, bulimia or refusal to eat that cannot be corrected, falls, fever, frequent urination, weight loss, and other physical discomforts, the patient should be sent to the hospital in time for re-evaluation by the doctor, and the treatment plan may be adjusted.
3. If there are cholinesterase inhibitors (donepezil hydrochloride, rivastigmine bitartrate, galantamine) in the medication taken out of the hospital, the patient’s pulse needs to be counted frequently. If it is less than 60 beats/minute, the medication needs to be stopped and timely medical treatment is required; if antipsychotic drugs (risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine fumarate, etc.) are taken out of the hospital to control mental symptoms, in addition to the need to return to the doctor every 1-2 months to evaluate mental symptoms, adjust the drug dosage or stop the drug in time, you should also observe whether the patient has side effects such as unsteady walking, body stiffness or crookedness, choking when swallowing, excessive sleepiness, etc.; if there are hypnotic drugs (such as estazolam, zopiclone, zolpidem tartrate, midazolam maleate, etc.) in the medication taken out of the hospital to improve sleep, the elderly need to be closely watched at night to prevent falls. In principle, these drugs should not be taken for a long time and need to be returned monthly for adjustment according to the doctor’s advice. At each follow-up visit, the doctor should be informed of the full list of drugs and the conditions observed.
4. In addition to taking medication according to the medical instructions in the discharge instructions and the instructions of doctors and nurses, after discharge, whether at home or in a specialized nursing institution, a barrier-free environment must be created for the patient, that is, an environment that makes the patient feel comfortable and safe, where they can move freely, not easily get lost, and not easily bumped into anything. In addition to the usual care from their relatives, they must also be more patient and communicate more with the patients. The principle of conversation should be to make the patients emotionally stable and happy. There is no need to emphasize right or wrong. Those who are no longer able to communicate verbally can provide companionship or touch to improve the patient’s mood. Maintain a regular schedule and encourage participation in family and social activities and hobbies within a safe range. Mild to moderate patients can consciously play educational games, such as playing cards, building blocks, doing handicrafts, singing, etc.
5. The best department to visit is a cognitive specialist or memory clinic . You can also choose a neurologist , psychiatrist or geriatrician who specializes in cognitive impairment. In order to ensure the continuity of treatment and save medical resources, it is not recommended to frequently change hospitals and doctors. It is best to go to a regular hospital close to home and convenient for treatment, and find a cognitive specialist you are relatively familiar with and trust for medical treatment and follow-up. If a referral is required due to changes in the condition, the doctor will usually recommend or discuss the next treatment location with you.
Nursing
1. Daily care
Family members should create a clean, quiet and comfortable living environment for patients. Supervise and assist patients to maintain good personal hygiene habits, pay attention to the care of urination and defecation, and reduce the chance of infection. Patients in the middle and late stages often lose the ability to take care of themselves and need careful care from their family members, including cutting nails (toenails), cutting hair, and drying bedding. And add or remove clothes in time according to climate changes. Those who have been bedridden for a long time should be turned over and their backs should be tapped regularly to prevent pressure sores and pneumonia. Supervise patients to go to bed on time, including taking a nap at noon, to ensure that they have enough sleep time every day, and try to create a quiet, comfortable and good sleeping environment for patients, but patients should be encouraged to move appropriately during the day, especially outdoor activities.
2. Safety care
Elderly people who are at risk of getting lost should be accompanied when they go out. Communication devices such as mobile phones and GPS locators can be used to keep track of the elderly’s location at any time; cards with home addresses and guardians’ contact information can be sewn on the elderly’s clothes. If an elderly person accidentally gets lost, call the police as soon as possible. Keep the floor flat and non-slip to avoid falls. The bed should be low, and bed guards can be added if necessary. Use a sitting toilet and non-slip floor in the bathroom. Be careful not to get burned when taking a bath. Toxic and harmful items should be placed in a locked cabinet to avoid ingestion. Sharp objects and sharp tools should be placed in a hidden place to avoid hurting others or yourself.
3. Nursing for cognitive impairment
Prepare memos for elderly people with memory loss. Encourage patients to watch TV and newspapers at appropriate times, and explain texts, pictures, and objects. Encourage patients to recall past life experiences frequently. Gently and considerately induce patients to express themselves in words. Activities can be arranged according to hobbies and remaining abilities. Physical activities: walking, practicing big pole, swinging upper limbs, doing health exercises, etc. Household activities: picking vegetables, washing vegetables, preparing chopsticks, washing dishes, wiping tables, etc. Nostalgic activities: watching and talking about old photos, listening to old songs, watching old movies, talking about the past, etc. Handicraft activities: origami, weaving, stringing beads, coloring, painting, etc. Educational activities: board games, jigsaw puzzles, building blocks, filling in lyrics, classifying items, etc. Gardening activities: planting, watering, touching flowers, smelling flowers, making decorations with plants, etc. Guidance and encouragement should be given during the activities, and the difficulty should be adjusted in time, and more encouragement should be given to give patients confidence.
4. Drug care
Take the medicine on time and in the prescribed amount strictly according to the doctor’s instructions. Some patients refuse to take medicine under the influence of delusions, hide medicine, and spit it out. Caregivers should strictly check and carefully examine the patient’s mouth, cup, and hands. Closely observe the adverse reactions of the medicine, such as orthostatic hypotension, dysphagia, coughing when eating, choking, constipation, urinary retention, etc. Caregivers should communicate with the doctor in time when they find it, so that it can be properly treated in time.
Rehabilitation
Based on the comprehensive assessment of the elderly, personalized and targeted physical rehabilitation methods are selected according to the patient’s physical and cognitive functions.
1. For patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease, appropriate exercise 3-5 times a week can help improve the patient’s physical fitness, cognitive function and ability to maintain daily life. Recommended exercise methods:
(1) Table tennis: Elderly people who have a hobby and foundation for table tennis and whose physical condition allows can play table tennis for 30 minutes every day.
(2) Power bicycle exercise: 40 minutes each time, which is beneficial to improve patients’ cognitive ability.
(3) Brisk walking: The pace should be no less than 3 km per hour, and this can be completed in several sessions of one hour per day.
(4) Tai Chi: At least 30 minutes a day can improve reaction ability, daily living ability, improve cognition, improve balance and prevent falls.
(5) Perform rhythmic exercise with music: improve falling conditions and increase strength and endurance.
(6) Practice bouncing a ball while walking: This can improve balance.
(7) Playing tennis: For the elderly who have a hobby and foundation in table tennis and whose current physical condition allows, playing tennis twice a week can prevent osteoporosis, enhance strength and reaction ability, and improve cognitive function.
2. For patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease, who have severe disability at this stage and are bedridden or have difficulty swallowing:
(1) Provide the patient with food and fluids of the nature requested by the therapist.
(2) Generally, patients need to sit up when eating unless the therapist has special requirements.
(3) Encourage patients to eat in small bites.
(4) Allow patients adequate time to eat;
(5) When feeding more food, make sure the patient has swallowed the previous mouthful of food completely.
(6) If the patient chokes, stop feeding immediately. If the choking does not subside within a short period of time, send the patient to the hospital for emergency treatment if necessary.
(7) Generally, the patient is allowed to sit and rest for 20 to 30 minutes after a meal.
(8) Passive and active limb movements, encouraging maximum range of motion while ensuring safety to avoid muscle contracture or other complications.
Nutrition
1. Ensure a diverse and balanced diet. Eat the right amount of calories to maintain a healthy weight. Pay attention to protein intake and ensure that half of your food is high-quality protein. Eat an egg a day and eat animal food in moderation. Among animal foods, fish has a low fat content and is easy to digest, making it very suitable for the elderly. Drink milk or dairy products every day to increase calcium intake. Eat a small amount of soy products every day. Avoid consuming too much fat and cholesterol. A certain amount of coarse grains can be included in the staple food every day, and eat more fresh vegetables and fruits. Eat small meals frequently, and the food should be soft and easy to digest. The diet should be light and low in salt, and steaming, boiling, stewing and other cooking methods should be used more often.
2. The food should be non-irritating, boneless, easy to digest, less greasy and easy to chew.
3. As the disease progresses, patients will have some eating problems, such as eating more, eating less, or refusing to eat.
(1) Hyperphagia is manifested as hyperphagia. The patient forgets to eat right after eating. Excessive eating leads to weight gain. The treatment method is to limit the patient’s food intake skillfully. Distracting the patient’s attention is a good way. If the patient wants to eat again right after eating, the caregiver can take the elderly to do other activities. Because the elderly eat a lot, they should eat more light foods in their diet to prevent excessive calorie intake. The patient can be allowed to eat appropriate high-fiber, low-calorie vegetables to make the patient feel full. In addition, the elderly eat more food gluttonously, so they should increase their activity level appropriately to increase consumption and maintain a balance between eating and moving.
(2) Eating less or refusing to eat means that the patient gradually loses the need to eat, refuses to eat or eats too little, leading to malnutrition. For such elderly people, it is necessary to arrange a personalized diet and improve the patient’s eating environment. Caregivers are required to pay more attention to the patient’s diet and increase the elderly’s dietary intake as much as possible by adjusting the variety, color, and taste of the meal.
(3) Some patients with severe dementia may have difficulty swallowing. In terms of diet, attention should be paid to adjusting the properties of food, and some special products for dysphagia can also be taken orally. If the above efforts still cannot ensure the nutrition of the elderly, it is necessary to provide the patient with necessary nutritional support under the guidance of a professional nutritionist. The most commonly used method is to ensure the patient’s dietary intake through enteral nutrition such as nasogastric feeding or gastrostomy.
4. The eating environment should be quiet and clean. Patients should sit down and the head of the bed should be raised 30-45 degrees. The food should be at a moderate temperature. The patient should not eat too fast. One teaspoon at a time. The patient should be fed the next mouthful after swallowing. For patients with severe dementia, family caregivers should assist the patient in eating to avoid obstruction and suffocation.
Protect your eyes for the elderly, start now!
Take care of your eyes, start from now!

With the increase of age, the degeneration of eyeball structure and the influence of bad eye habits, the eye health problems of the elderly are becoming more and more obvious. How should the elderly take care of their eyes? With the arrival of National Eye Care Day, let’s learn about it together!
Avoid prolonged use of the eyes

Some elderly people do not like to go out or have limited mobility, so they can only move around indoors or in bed, which results in watching TV and playing with mobile phones becoming their main pastime every day. Here is a reminder for everyone: do not use your eyes for a long time!
In order to see nearby objects clearly, our eyes will contract the ciliary muscles. If the ciliary muscles do not get a rest for too long, the burden on the eyes will be increased, thus causing eye diseases. So please remember: after using your eyes for 40 minutes to 1 hour, you should relax for 5 to 10 minutes by looking into the distance, closing your eyes, or doing eye exercises.
Pay attention to the lighting environment when using your eyes

Some elderly people have a strong sense of thrift and are often reluctant to turn on the lights when watching TV or using their mobile phones at night. In fact, in a dark environment, the light emitted by electronic screens can cause a relatively large stimulation to the eyes. On the contrary, if you read books or newspapers in a bright outdoor place, it will also damage your visual function, causing dry eyes, sore eyes, and even tears. Therefore, when using your eyes for a long time, you must pay attention to the impact of ambient light on your eyes.
Avoid using handkerchiefs
Or rub your eyes with your hands

Rubbing your eyes can easily cause bacterial infection in the eyes. If your eyes are uncomfortable, you can wash your hands first, then close your eyes and press gently. When problems such as dry eyes and increased secretions occur, you should seek medical attention in time, buy regular eye drops, take correct eye drops, and use symptomatic medication.
Get regular eye exams
Elderly people often suffer from eye problems due to chronic diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy; people with high blood pressure and thrombosis often suffer from retinal vein occlusion; emotional excitement, mental stress, and excessive fatigue may induce glaucoma, etc. Therefore, the elderly should pay more attention to eye examinations, and achieve early monitoring, early detection, early warning, and early intervention.
Wear glasses correctly

When you need to wear glasses or sunglasses, you should buy them from a regular optician after testing and evaluation. At the same time, you should promptly provide feedback to your doctor about your experience after wearing them and have regular checkups.
Nutritional supplements to prevent eye diseases

Eat a balanced diet and eat more foods rich in lutein, such as corn, broccoli, carrots, tomatoes, etc.
Take rest
With acupressure

Closing your eyes and resting your mind can not only give your eyes a full rest, but also relieve the pressure of using your brain. You can also gently massage the acupuncture points around your eyes, such as pressing the Jingming acupoint: every morning and evening, press the thumb and index fingertips in the depression above the inner corner of the eye, first press down, then squeeze upwards, for 10 minutes each time, once a day in the morning and evening.
Talk about falls among the elderly
Falls in older adults are a common but serious problem that can lead to fractures, decreased physical function, and psychological distress. Understanding the causes and prevention of falls is critical to the safety of older adults.
Causes of falls in the elderly
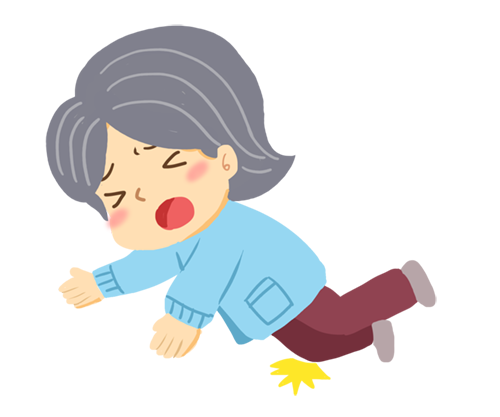

A fall is a sudden, involuntary, unintentional change in body position, falling to the ground or a lower plane. According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), falls are classified into the following two categories: ① Falls from one plane to another (lower) plane; ② Falls on the same plane. Falling out of bed, falling to the ground when standing up from a wheelchair, etc. are all considered falls.
Risk factors for falls include physical factors, mental factors, drug factors, disease factors and environmental factors.
(1) Physical factors:
The decline in gait coordination, balance stability and muscle strength in the elderly, as well as the decline in vision, hearing, vestibular function, proprioception, and the decline in urinary and bowel control ability are all risk factors for falls.
(2) Mental factors:
Psychiatric problems such as dementia, delirium, abnormal behavior, and confusion can precipitate falls.
(3) Drug factors:
Drugs are another important cause of falls in the elderly. Taking sedatives, antipsychotics, antihypertensives, vasodilators, hypoglycemic drugs, etc. can easily lead to changes in consciousness, spirit, and blood pressure, thereby affecting the balance function and causing falls. The coexistence of multiple diseases in the elderly and multiple medications are also risk factors for falls in the elderly.
(4) Disease factors:
Elderly people often have multiple diseases. Acute and chronic diseases such as nervous system diseases, cerebrovascular diseases, cardiovascular diseases, bone and joint diseases, diabetes, etc. can cause dizziness, unstable gait, imbalance, weakness, visual or consciousness disorders, thus inducing falls. Many elderly people have psychological disorders such as depression, anxiety, fear, etc., which are manifested as inattention, unwillingness to accept old age, and unwillingness to trouble others. They also try to do things that are beyond their ability by themselves, which significantly increases the risk of falls.
(5) Environmental factors:
Environmental factors that cause falls include the floor, lighting, furniture, clothing, facilities, etc. Wet and uneven floors, loose carpets, overly slippery floors, small indoor spaces, improper placement of items, too dark or too strong light, inappropriate step heights, seats and beds that are too high, too low or too light, toilet chairs without safety handrails and non-slip mats, inappropriate clothing, pants that are too long or too loose, shoes that are not the right size, shoes that are not non-slip, and walking in slippers are all factors that can easily cause falls.
What are the serious consequences of falls in the elderly?

(1) Physical aspects:
22% to 60% of the elderly have been injured due to falls. The mildest injuries include hemarthrosis, dislocation, sprain and hematoma; the severest injuries include fractures, including fractures of the hip, surgical neck of humerus and distal radius, and compression fractures of the spine. The most serious ones are craniocerebral injuries, which can directly lead to death.
(2) Functional aspects:
Elderly people who fall and get injured usually need to stay in bed or have their limbs immobilized for a long time, which can lead to muscle atrophy, osteoporosis, and even joint contractures, seriously affecting limb function.
(3) Psychological aspects:
50% of people who fall develop a fear of falling again. The fear of falling can lead to a vicious cycle of falling → loss of confidence → fear of moving → weakness → more prone to falling, and even becoming bedridden.
Elderly people with reduced mobility
How to prevent falls?
01

Help the elderly understand their own mobility and act within their capabilities.
02
When moving, body position should be changed slowly, and if necessary, assistive devices (such as various types of crutches, walkers, wheelchairs) or help from family members should be used.
03

Wear appropriate corrective devices (glasses, hearing aids, etc.) and adjust them regularly.
04

Adjust your lifestyle, drink less water before going to bed, develop a habit of going to the toilet on time, and practice urination control training.
05

For elderly people with mobility impairment, a toilet should be prepared at the bedside, and nursing pads, external drainage devices or diapers should be used when necessary. Elderly people with cognitive impairment need caregivers to assist in training and improve their nighttime toileting methods, and choose to use bedside commode chairs, bed toilets, etc., to reduce the frequency of leaving bed and reduce the risk of falling.
06

Balance training: The elderly can be helped to do Tai Chi, standing on one leg with a chair, and other exercise training according to their degree of cooperation.
Mentally unstable elderly people
How to prevent falls?
01

When the elderly are emotionally unstable, they should be comforted in time, have someone accompany them, reduce their activities and prevent falls.
02

Urge the elderly to take medicine on time and pay attention to adverse reactions after taking medicine.
03

Keep the furniture as simple as possible and avoid sharp corners. Leave enough space for walking in the activity area and avoid stacking too much clutter or small objects that could easily trip the elderly.
04

Place items in a fixed position to keep dangerous items away from the elderly. Use anti-slip materials or anti-slip treatment on the ground. If there is water on the ground, wipe it off in time. Give elderly people with cognitive impairment non-slip and well-fitting shoes to prevent them from falling.
05
When the elderly lie in bed, they should draw the bed rails, have armrests and backrests on the seats, and use seat belts for protective restraint when necessary.
How to prevent falls caused by medications?
01

Antihypertensive drugs can easily cause dizziness. It is recommended that the elderly monitor their blood pressure regularly and move slowly and within their ability when changing body positions.
02

Blood sugar lowering drugs can cause hypoglycemia, which manifests as dizziness, fatigue, and palpitations, leading to falls. It is recommended that the elderly monitor their blood sugar regularly, and caregivers should remind the elderly with cognitive impairment to eat on time and help them eat in time when hypoglycemia is found. It is not advisable to exercise on an empty stomach.
03

Sedatives, hypnotics, antipsychotics, etc. can easily cause drowsiness, dizziness, fatigue, unstable gait, etc., which may lead to falls. It is recommended to assist the elderly in washing, going to the toilet, etc., and take the medicine after the elderly go to bed. Try to avoid leaving the bed after taking the medicine, and use the toilet next to the bed or on the bed at night.
Preventing Falls
How should the home environment be arranged?
(1) Ground:

The floor material should be non-slip and non-reflective; tile carpets should not be used; activities should be suspended after wet cleaning the floor, and safety warning signs should be placed; the passages should be wide and unobstructed.
(2) Lighting:

The light from the lamps is sufficient, soft and not dazzling; turn on the night light at night.
(3) Furniture:

The items in the room are placed in a fixed position, and the height of the bed should be such that the feet of the elderly can reach the ground when sitting on the edge of the bed; provide a chair with good stability and armrests.
(4) Facilities:

Bathrooms and toilets should be equipped with handrails, non-slip floors, outward-opening doors, and toilets should be 42 to 45 cm high. Bathrooms should be equipped with bath chairs. Toilets should be at an appropriate height; table corners and window sills should be rounded or covered with protective stickers.
Preventing falls among the elderly is a topic we have always been concerned about. Let us work together to care for the health of the elderly and pass on the relay of love!
Hand Exercises for dementia
1. Press your fingers together to express love for each other. Do this 10 times.

2. Make a fist and stretch, and exercise repeatedly. Do this 10 times.

3. Cross your fingers and keep your mind clear. Do this 10 times.

4. Swing inward and outward, left and right. Do this 10 times.
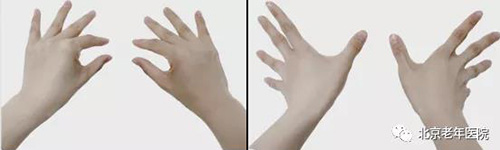
5. Clasp your fingers together and turn your wrist. Do this 10 times.

6. Fight with fists and palms to strengthen your body. Do this 10 times.
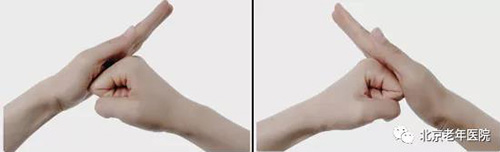
You can practice all or some of the finger exercises every day according to your own situation. This will not only prevent Alzheimer’s disease, but also have a very positive effect on reducing the incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Articles
(scroll for more)
Rehabilitation training for Parkinson’s disease is very important! Follow me and practice!
These 10 points are very important to control blood pressure
Flu season is coming, are you ready?
To prevent respiratory infectious diseases, wear masks
Home care of the pocket after permanent pacemaker implantation in elderly patients
How to prevent pressure sores in bedridden elderly people
How can the elderly avoid aspiration during daily eating?
Vegetables come in many colors, eat a wide variety and get enough nutrition
How much do you know about home oxygen therapy?
Let’s talk about high blood pressure and heart rate
Alzheimer’s disease discharge health prescription
Talking about falls among the elderly